


Stable Red-Emissive Cationic Dithienotropylium Dyes
K. Asai, A. Fukazawa, S. Yamaguchi, Chem. Eur. J., Early View.
[DOI: 10.1002/chem.201604509]
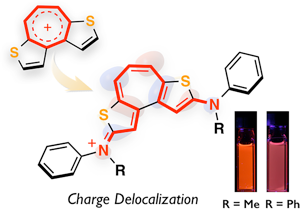
カルボカチオンは,様々な化学反応における中間体であるのみならず,機能性色素の基本骨格として重要な化学種である.特に,電子供与基によって安定化されたカルボカチオンは,可視光領域に強い光吸収や蛍光発光を示すことから,バイオイメージング用蛍光色素として重宝されている.このような機能性蛍光色素の分子設計について重要なのは,いかに安定なカルボカチオンを実現するかである.このような観点から今回我々は,芳香族性をもつ7員環カルボカチオンであるトロピリウムイオンに着目し,チオフェン縮環部位と電子供与性のアミノ基を導入することにより,極めて安定なカルボカチオンを得ることに成功した.X線結晶構造解析により,アミノ置換ジチエノトロピリウムイオンは顕著なキノイド性をもち,ポリメチン色素用の電子構造をもつことを明らかにした.このような電子構造を反映して,これらの化合物は可視光領域に比較的強い光吸収および蛍光を示し,その蛍光発光は赤色領域に及ぶ.一連の結果から,トロピリウムイオンが安定なカチオン性色素の基本骨格として有用であることを示すことができた.
A series of thiophene-fused tropylium ions, containing various electron-donating amino groups at the terminal positions, was synthesized. The fusion of the thiophene rings, as well as the presence of the terminal amino groups endows the cationic tropylium ion with excellent stability and high pKR+ values. X-ray crystallographic analysis of these compounds revealed a pronounced quinoidal character for the amino-substituted dithienotropylium skeletons. These compounds exhibit attractive photophysical properties such as strong absorption in the visible region combined with red fluorescence. Theoretical calculations suggested that the 3,3′-bithiophene substructure should be crucial for attaining these photophysical properties.
発光性のトロピリウムイオン
2016/10/20
