


Photodissociation of B–N Lewis Adducts: A Partially Fused Trinaphthylborane with Dual Fluorescence
K. Matsuo, S. Saito, S. Yamaguchi, J. Am. Chem. Soc., accepted for publication.
[DOI: 10.1021/ja506980p]
ホウ素–窒素錯体の光解離による二重発光の実現
2014/08/28

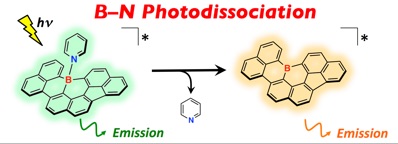
三配位ホウ素原子を含む有機化合物は、ホウ素の空軌道に由来したルイス酸性を示し、含窒素ヘテロ環などの非共有電子対をもつ分子とルイス酸塩基対を形成する。近年、分子内にホウ素–窒素配位結合をもつp共役化合物の特異な光反応性が報告され、新たなフォトクロミック材料としての期待が高まっている。一方で、それらの変化は主にホウ素–炭素結合の転位によるものであり、ホウ素–窒素結合の切断は起こらない。これに対して我々は、平面固定されたトリナフチルボランを新たに合成し、そのピリジン錯体の光物性を詳細に検討したところ、光励起状態においてトリナフチルボランとピリジンへ解離するという、ホウ素–窒素配位結合を有するルイス酸塩基対の新たな光反応性を見出した。この反応は、等電子構造であるトリアリールメタンロイコ色素の光照射によるカルボカチオンの生成に類似していると考えられる。部分的な縮環構造をもつ平面固定トリナフチルボランは当研究室でこれまでに合成した平面固定ボランに比べて高いルイス酸性をもち、室温でもピリジンと錯体を形成する。ピリジン錯体は、光励起により錯体からの蛍光と解離した三配位の状態からの二重発光性を示す。また、ルイス塩基性を変えたピリジン誘導体との錯体の検討を行ったところ、光解離の挙動は大きく変化し、ルイス塩基性に大きく依存する事を見出した。
We have synthesized a partially fused trinaphthylborane. The small structural constraint imparts high Lewis acidity to the planarized triarylborane skeleton, while the remarkable stability towards water and oxygen is maintained. Consequently, the molecule can easily form Lewis adducts in solution, even with weakly Lewis basic pyridine derivatives. Importantly, these B–N Lewis adducts undergo unprecedented photodissociation in the excited state, resulting in a dual emission that covers a broad range of the visible light (480–700 nm). This behavior strongly depends on the delicate balance between the Lewis acidity of the borane and the Lewis basicity of the additive. The photoinduced B–N bond cleavage and the regeneration of the highly stable boron-embedded p systems should have great potential as a basis for various functions, such as photochromism, organocatalysis, and photoresponsive supramolecular assembly. Further studies exploring these possibilities are currently undertaken in our laboratory.